Across industries, engineers are increasingly turning to continuous fiber reinforced (CFR) thermoplastic composites. These materials bring together lightweight properties, exceptional mechanical performance, and environmental benefits—making th...
Contact Us
Across industries, engineers are increasingly turning to continuous fiber reinforced (CFR) thermoplastic composites. These materials bring together lightweight properties, exceptional mechanical performance, and environmental benefits—making them a strong contender to replace metals and traditional thermoset composites.
Reducing the weight of a product can significantly lower its energy consumption and related CO₂ output, particularly in the transport sector. CFR thermoplastics deliver on both fronts: they’re low in density yet strong enough to use in smaller quantities, amplifying the weight-saving effect.
The production process requires no curing, generates no harmful emissions, and supports recycling—offering a cleaner footprint compared to many conventional materials.
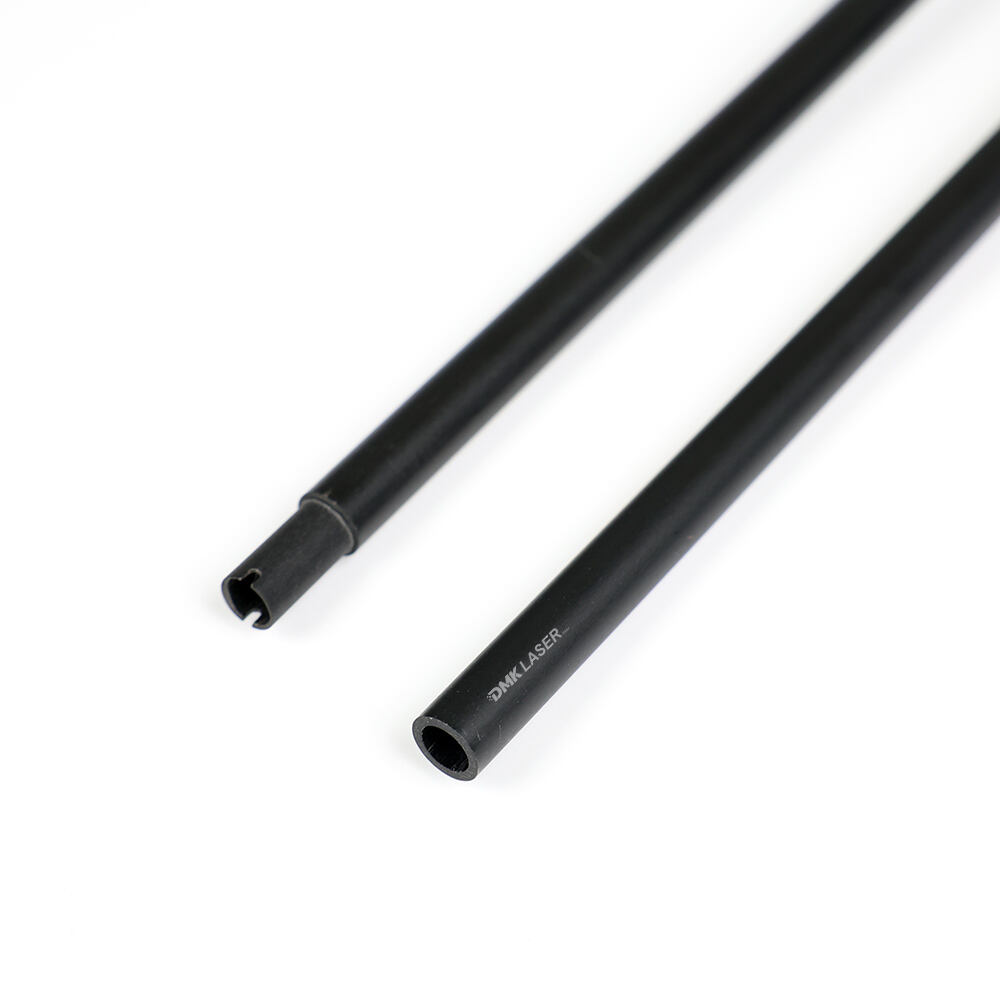

Surgical robot instrument rod
When it comes to strength, stiffness, and reliability in challenging environments, CFR thermoplastics stand out. They resist corrosion, chemicals, and wear, all while maintaining performance over long operational lifespans. They also absorb shocks and dampen vibrations better than most metals, improving both product performance and user comfort.
Performance advantages include:
Significantly lighter than steel
High strength-to-weight ratio
Strong resistance to fatigue
Excellent impact and vibration absorption

Subsea/Land Oil Pipeline
Whether in a vehicle, a piece of sporting equipment, or precision machinery, vibration can shorten component life and harm user experience. Thanks to the viscoelastic nature of thermoplastics, CFR versions excel at damping vibrations, reducing fatigue on both the equipment and the operator.

High speed motor rotor sleeve
In the event of breakage, CFR thermoplastics are less likely to create sharp or hazardous debris. Their layered fiber structure also dissipates high levels of impact energy, helping to shield nearby parts and reduce the risk of secondary damage.
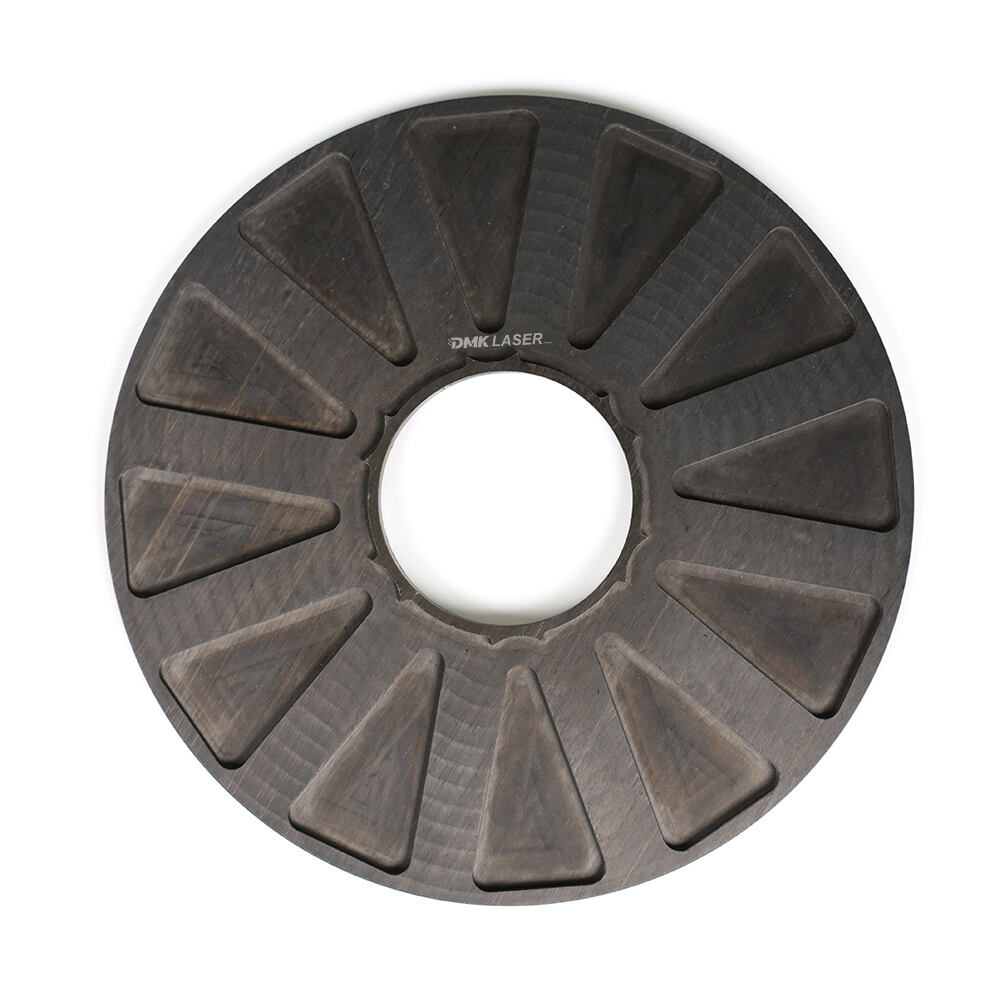

Axial flux motor stator housing
Thermoplastic composites can be reheated and reshaped, opening up opportunities for design simplification and part integration. This flexibility can reduce assembly steps, lower production costs, and improve recyclability at the end of service life.
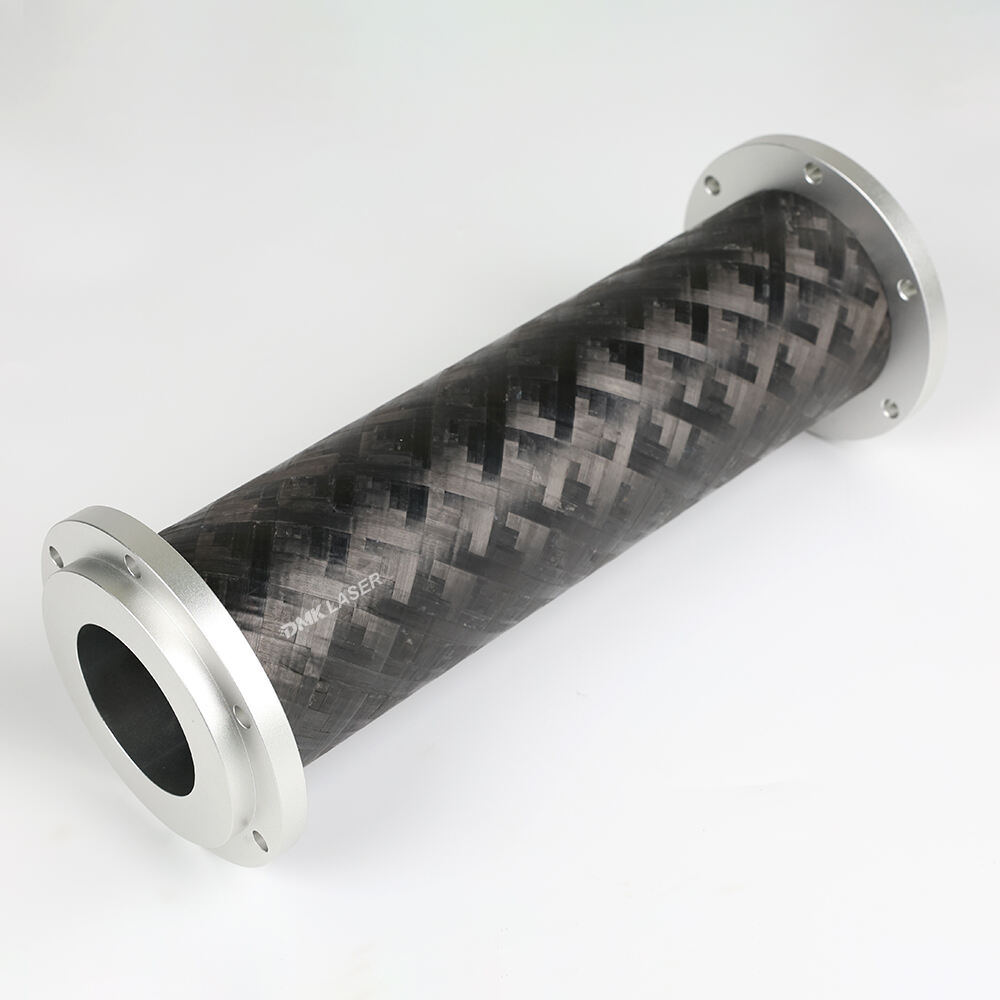

Power transmission shaft
With their ability to be reused and recycled, CFR thermoplastics fit neatly into the Reduce–Reuse–Recycle approach. Modern manufacturing methods, such as additive winding, help minimize raw material waste, while ongoing developments in bio-based polymers and natural fibers are expanding the sustainability potential even further.
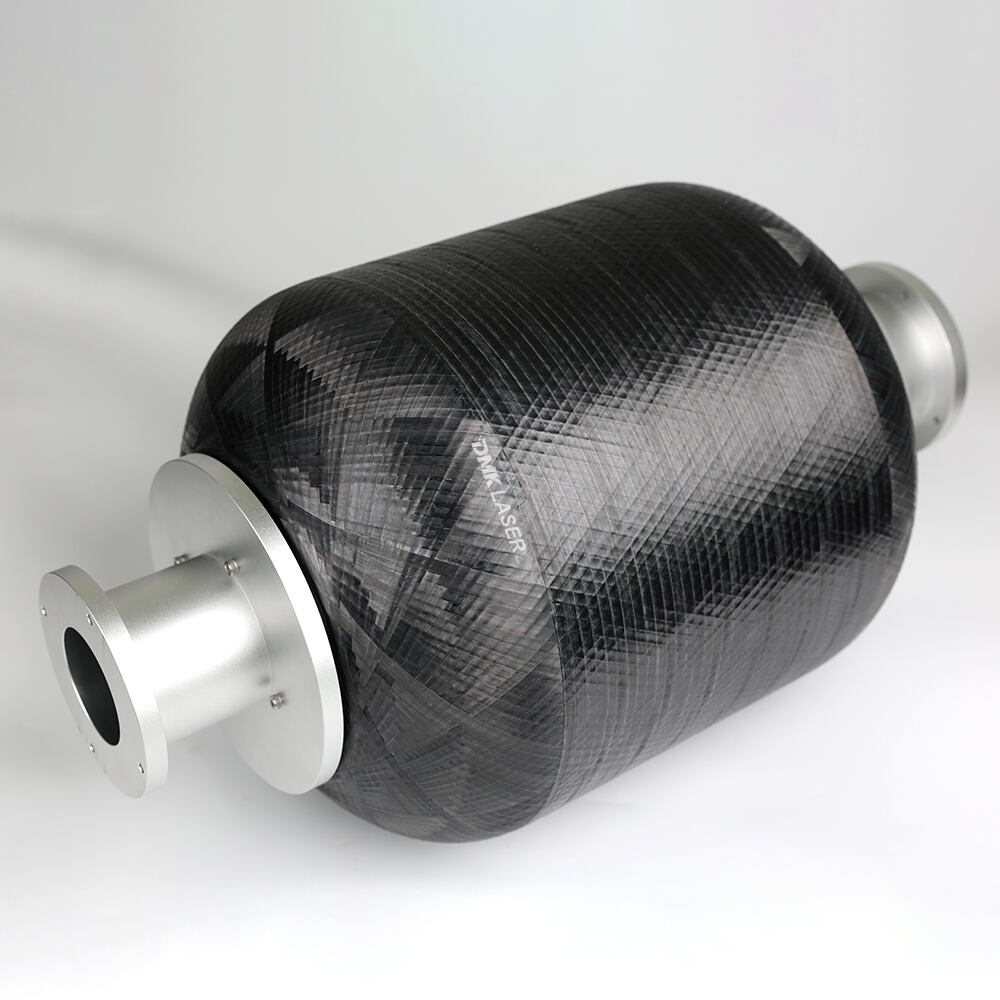

Pressure vessel/hydrogen storage bottle
Bottom line
CFR thermoplastic composites offer a rare combination of light weight, strength, sustainability, and design adaptability. For companies seeking performance gains without compromising environmental responsibility, they represent one of the most forward-thinking material choices available today.
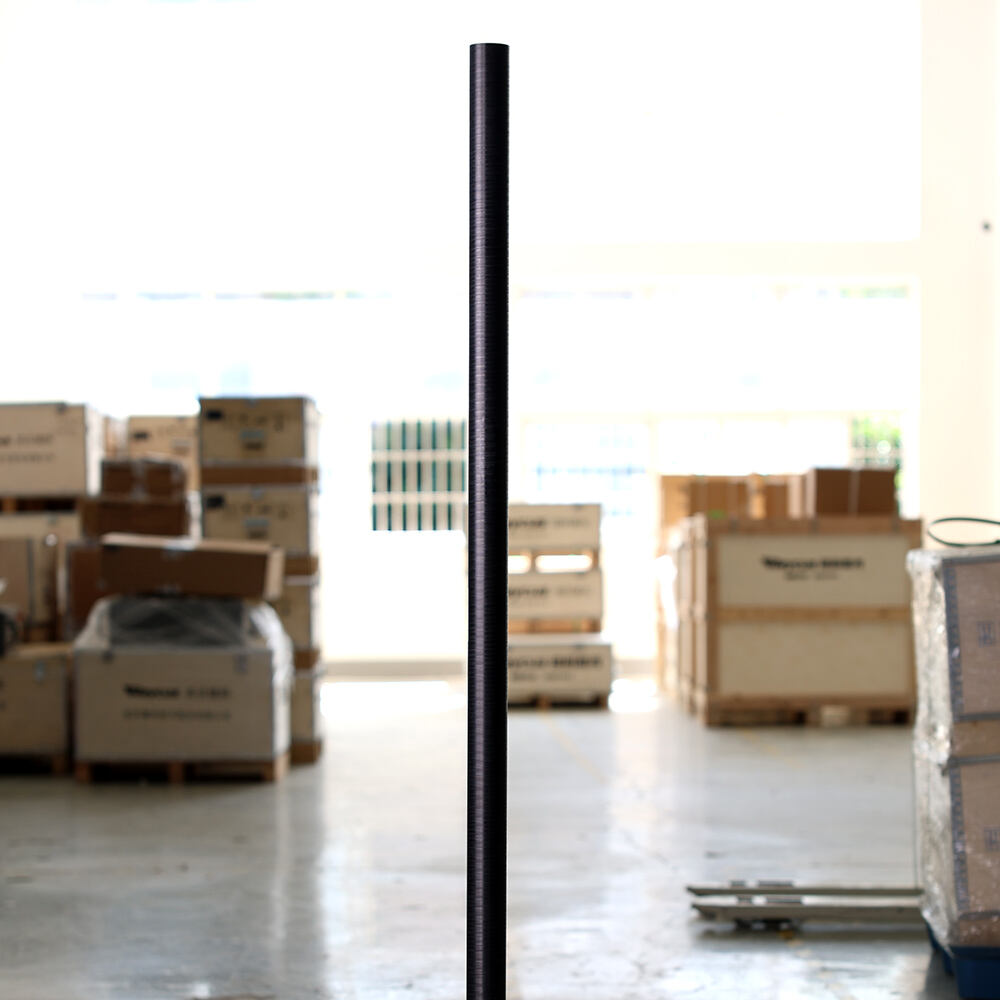

Carbon fiber sailboat mast