- Página Inicial
- Produtos
- Sobre Nós
- Vídeos
- Aplicação
- Notícias
- Central de Ajuda
- Contacte-nos
I. Pontos Críticos da Indústria na Remoção de Tintas Marítimas e a Introdução da Tecnologia a Laser Navios operam por longos períodos em ambientes marinhos altamente corrosivos, e seus revestimentos superficiais atuam como barreira crítica contra a corrosão. No entanto, esses revestimentos inevitavelmente envelhecem e...
Contacte-nos
I. Pontos Críticos da Indústria na Remoção de Tintas Marítimas e a Introdução da Tecnologia a Laser
Os navios operam em ambientes marinhos altamente corrosivos por longos períodos, e seus revestimentos superficiais atuam como uma barreira crítica contra a corrosão. No entanto, esses revestimentos envelhecem inevitavelmente e descascam com o tempo. A remoção regular da tinta e a repintura são processos essenciais para garantir a segurança do navio e prolongar sua vida útil. Atualmente, os métodos tradicionais amplamente adotados na indústria marítima — como esmerilhamento mecânico, jateamento de areia e limpeza química — mal conseguem atender aos requisitos básicos, mas apresentam desvantagens significativas: alta intensidade de mão de obra, poluição ambiental severa, consumo excessivo de recursos e dificuldade de automação.
Como as pesquisas indicam, os métodos tradicionais já não são compatíveis com as exigências da construção naval verde moderna. Em contraste, a tecnologia de remoção de tinta a laser, com suas vantagens únicas de operação sem contato, processo livre de poluição, alta precisão e facilidade de automação, surgiu como uma solução ideal para enfrentar os desafios de remoção de tinta marinha. Ela utiliza a interação entre feixes de laser de alta energia e revestimentos superficiais para alcançar a remoção precisa de tinta sem danificar o substrato.
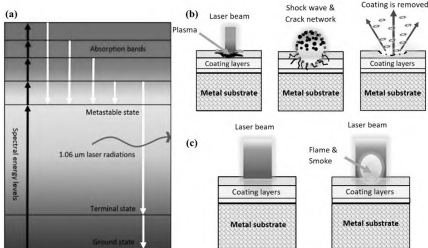
II. Núcleo da Tecnologia de Remoção de Tinta a Laser: Avanços na Pesquisa do Mecanismo e do Processo
1. Mecanismo Complexo de Remoção de Tinta
A aplicação bem-sucedida da tecnologia de remoção de tinta a laser depende de uma compreensão profunda do seu mecanismo subjacente. Estudos mostraram que a remoção de tinta por laser é um processo complexo que envolve múltiplos efeitos físicos, incluindo ablação térmica, ondas de choque de plasma e vibração por tensão térmica. Por exemplo, pesquisas realizadas por estudiosos como Lei Zhenglong revelaram que lasers de pulso milissegundo e lasers de pulso nanossegundo utilizam mecanismos dominantes diferentes: o primeiro baseia-se principalmente na combustão e vaporização, enquanto o segundo depende da vibração termoelástica. Isso fornece uma base teórica para selecionar equipamentos e parâmetros adequados de remoção de tinta a laser para diferentes revestimentos e substratos.
2. Parâmetros Chave do Processo
A pesquisa de processo atua como uma ponte entre limpeza a Laser tecnologia e aplicação prática. A literatura confirma que parâmetros como potência do laser, velocidade de varredura, frequência de pulso e distância de desfoque impactam diretamente a eficácia e eficiência da remoção de tinta. Por exemplo, um estudo de Madhukar et al. demonstrou que, com uma potência de laser de 300 W, a otimização da velocidade de varredura permite a remoção não destrutiva de tinta de superfícies de aço inoxidável.
Importante destacar que pesquisas confirmaram que a rugosidade superficial e a dureza do aço marinho tratado com tecnologia a laser para remoção de tinta atendem às normas internacionais (por exemplo, ISO 8501-1 Sa 2.5). Além disso, a adesão dos revestimentos repintados é superior ou equivalente àquela de superfícies tradicionalmente jateadas com areia, criando uma base sólida para pinturas subsequentes de alta qualidade.
III. Aplicações Práticas e Grande Valor da Remoção de Tinta a Laser na Indústria Marítima
A tecnologia de remoção de tinta a laser possui grande valor prático, especialmente para o processamento preciso de áreas planas do casco e espaços internos complexos da cabine.
Qualidade de Soldagem Aprimorada: Pesquisas realizadas por uma equipe da Universidade de Jiangsu mostram que o pré-tratamento superficial a laser da liga de alumínio 6061 reduz efetivamente a porosidade na soldagem e melhora a qualidade das soldas.
Processamento de Materiais Compostos: A tecnologia também é aplicável a compósitos de fibra de carbono, que são cada vez mais utilizados na fabricação leve de embarcações. A limpeza a laser otimiza as propriedades superficiais desses compósitos e aumenta a eficácia da adesão.
Reparação e Construção Verde de Embarcações: Diferentemente do jateamento com areia, que gera resíduos e poluição significativos, a limpeza a laser não requer agentes químicos nem consumo de abrasivos, concretizando verdadeiramente a fabricação sustentável.
IV. Desafios e Perspectivas: Rumo à Aplicação Industrial Madura
Apesar das suas amplas perspectivas, a aplicação em larga escala da tecnologia de remoção de tinta a laser na indústria marítima ainda enfrenta desafios:
Melhoria dos Modelos de Mecanismo: A universalidade dos modelos teóricos existentes para sistemas complexos de materiais requer pesquisas mais aprofundadas.
Baixa Inteligência do Processo: Adaptar inteligentemente os parâmetros do processo às variáveis condições de trabalho no local continua sendo um desafio fundamental.
Questões de Eficiência e Padronização: Atualmente, a eficiência de limpeza está aquém dos métodos tradicionais, e há uma falta de padrões unificados de avaliação de qualidade na indústria.
No futuro, o desenvolvimento da tecnologia de remoção de tinta a laser estará fortemente focado na automação e na inteligência. A integração de equipamentos de remoção de tinta a laser com robôs, posicionamento de alta precisão e tecnologia de monitoramento em tempo real para desenvolver sistemas integrados de limpeza inteligentes é uma tendência inevitável. Com os avanços em lasers de alta potência e alta qualidade de feixe, a eficiência de limpeza será significativamente melhorada.
V. Conclusão
Em resumo, pintura a laser tecnologia de remoção, caracterizada por sua natureza verde, precisa e controlável, demonstra um enorme potencial e valor de aplicação na indústria marítima. Não é apenas uma alternativa ideal aos processos tradicionais de limpeza de alta poluição, mas também uma tecnologia-chave que impulsiona a transformação e modernização da indústria marítima rumo à fabricação inteligente e sustentável. Com pesquisas aprofundadas sobre os mecanismos, otimização de processos e desenvolvimento de equipamentos inteligentes, a tecnologia de limpeza a laser está prestes a trazer uma profunda revolução tecnológica para a indústria marítima em um futuro próximo.